Thread
HW POV(线程的硬件执行): focus Core than GPU
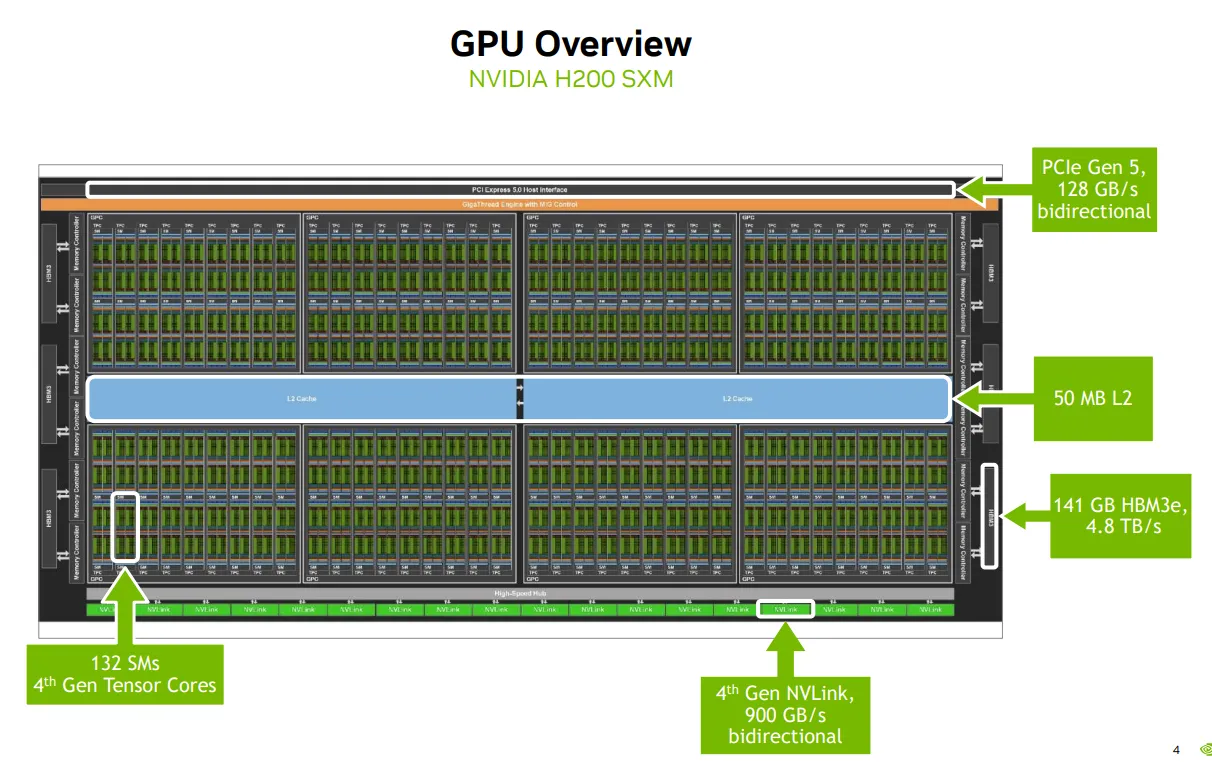
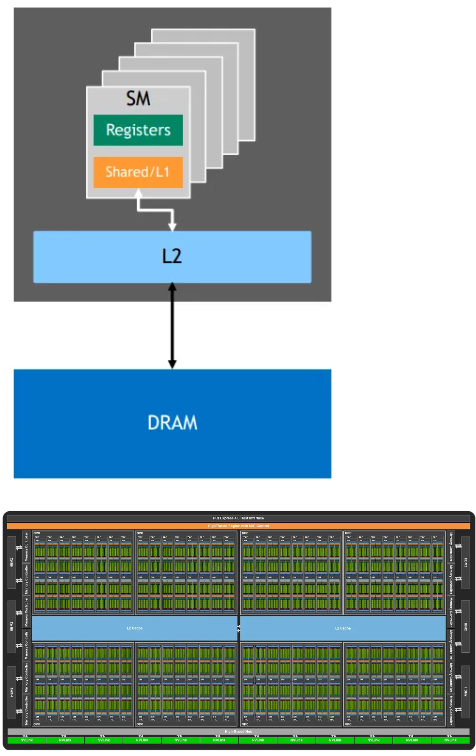
A GPU
COMP
|_2 division
|_4 GPC (Graphics Processing Cluster)
|_8 TPC (Texture/Processing Cluster)
|_2 SM (Streaming Multiprocessor)
MEM
|_other components
|_HMB3e + memory controller
|_L2 Cache
|_NVLink + High-speed hub
|_PCIE

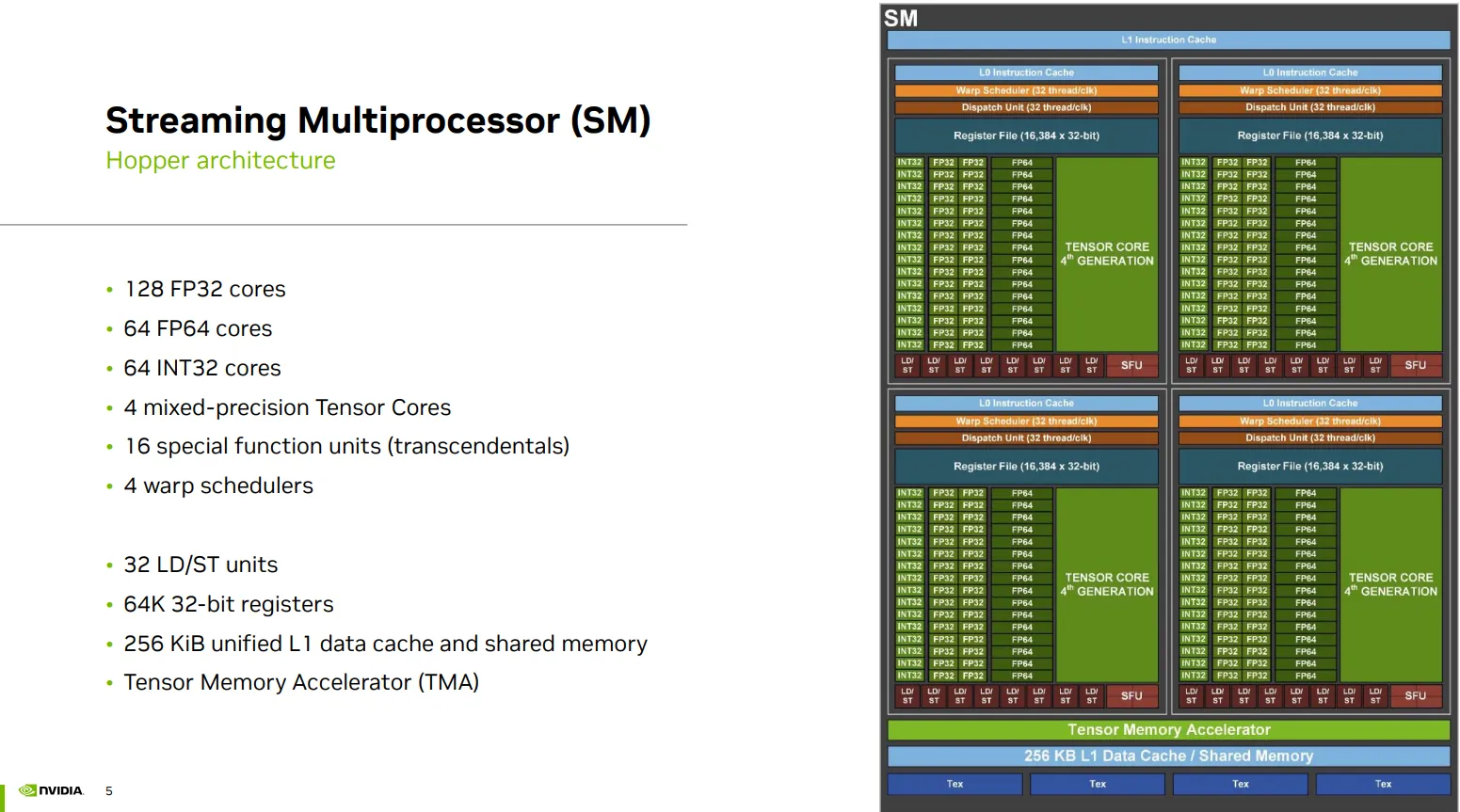
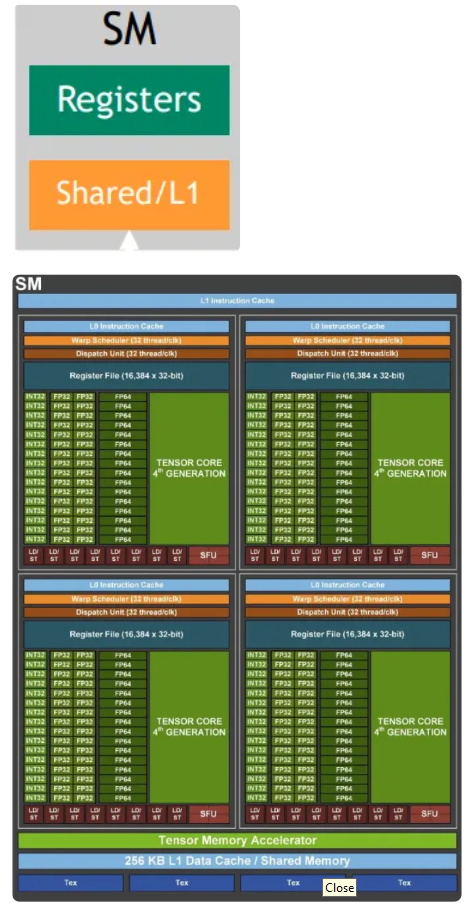
A SM
INST
|_L1 instruction cache
|_ 4 *
|_L0 instruction cache
COMP
|_ 4 *
|_Cores - 32 FP32 cores + 16 FP64 cores + 16 INT32 cores + 1 mixed-precision tensor cores
|_Units - 8 LD/ST units + 4 Special Function Units/SFU + 1 Dispatch unit
|_16K * 32 bit register file
|_Warp scheduler
MEM
|_256KB L1 data cache/shared memory
|_Tensor Memory Accelerator
Orchestration POV(线程的硬件调度): focus SIMT Architecture than Warp
Flynn’s taxonomy
程序设计角度 的模型(Program-Level)
- 是你怎么写代码
SPMD (Single Program Multiple Data)
- Single Program, Multiple Data:所有处理单元运行同一个程序,但处理不同的数据。
- 它是程序员写代码时的思维模型,比如 CUDA、OpenCL、MPI、OpenMP 都是 SPMD 风格。
- 每个线程/进程通过自己的 ID(如 threadIdx.x)来决定处理哪部分数据。
- 重点是“写一份代码,跑在多个数据上”。

硬件执行角度 的模型(Instruction-Level)
- 是硬件怎么执行它, 指令和数据的调度方式
| 模型 | 指令流 | 数据流 | 举例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIMD | 多指令 | 多数据 | 多核 CPU、分布式系统 |
| SIMD | 单指令 | 多数据 | Intel AVX、ARM NEON |
| SIMT | 单指令(每个 warp) | 多线程 | NVIDIA CUDA Warp |
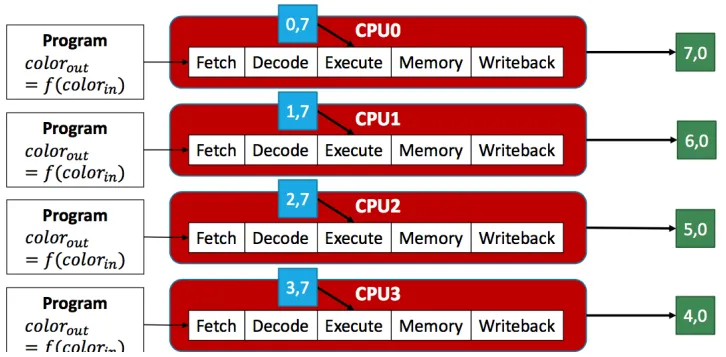
Running SPMD on MIMD (Multiple Instruction Multiple Data)
- Multiple Instruction: 线程可以运行不同的程序
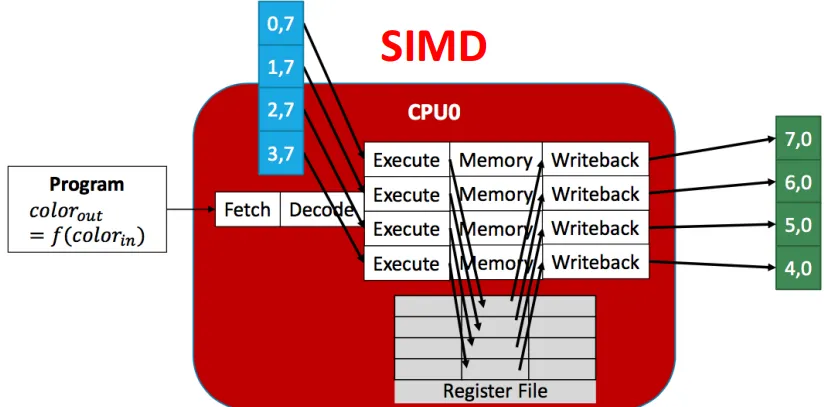
Running SPMD on SIMD(Single Instruction Multiple Data)
- Single Instruction: 所有线程运行相同的程序
- Multiple Data: 一个线程(single register file) + 数据通道(vector lanes)
Running SPMD on SIMT(Single Instruction Multiple Thread)
- Single Instruction: 所有线程运行相同的程序
- Multiple Thread: 每个线程处理不同的数据(独立的context, Multiple register files) + Scalar Ops
- 独立的程序计数器(PC)
- 独立的寄存器文件
- 独立的栈和局部变量
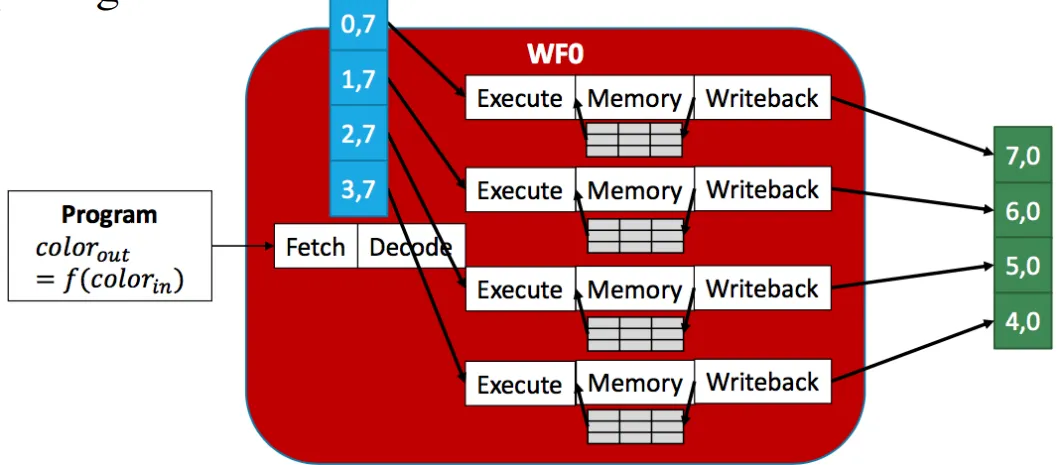
怎么高效调度SIMT定义的这些多个线程:Warp32个一起
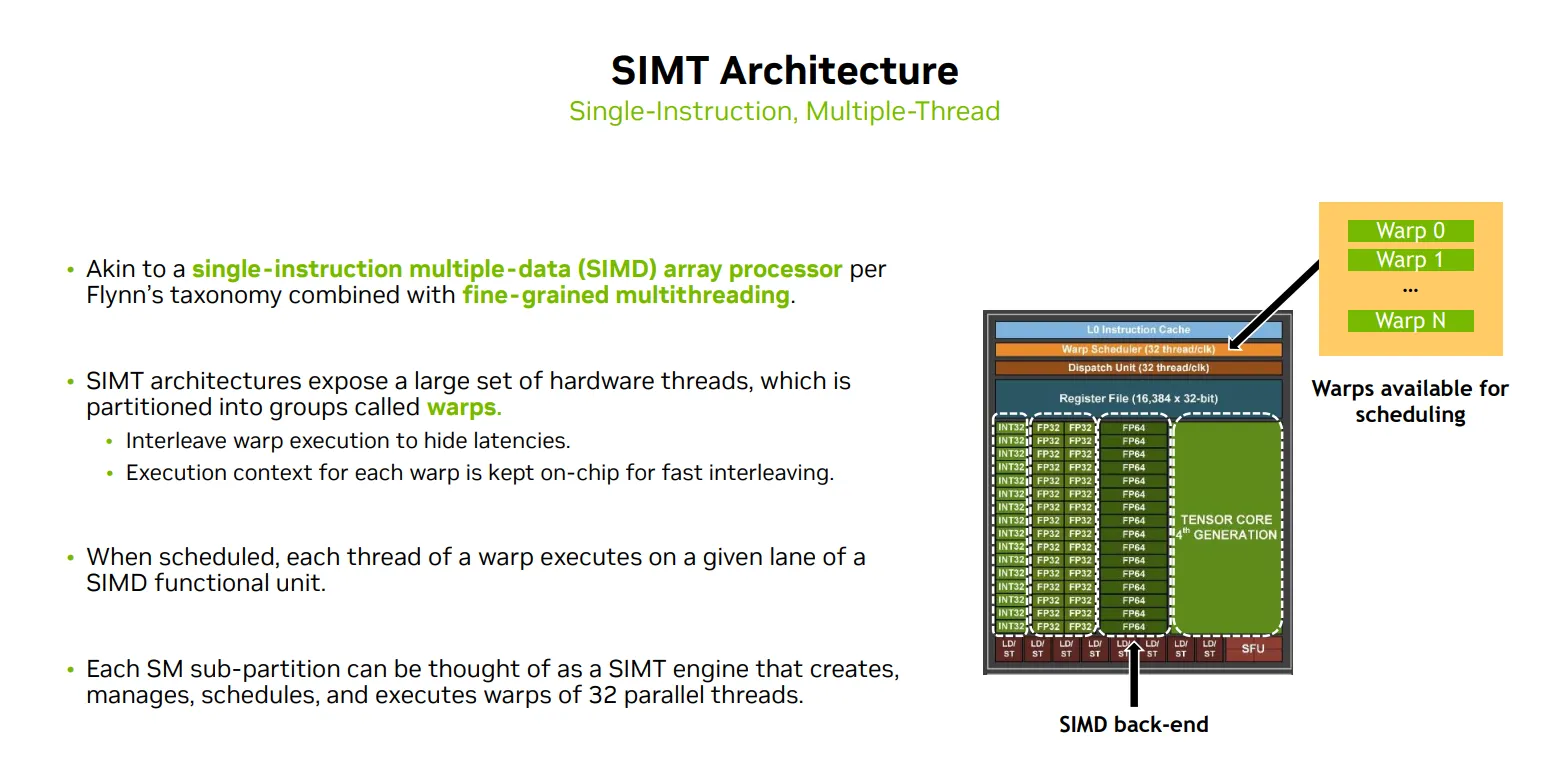
Threads are grouped into warps
- 每个 Warp有 32 threads
- 线程以 warp 为单位调度。
- Warps are interleaving to hide latencies
调度器的并发管理能力
- 一个 Warp Scheduler 最多可以同时追踪和管理 16 个活跃的 Warps。
- 这些 Warps 并不是每个时钟周期都在执行,而是处于“准备好被调度”的状态。
- 这样做的目的是为了隐藏延迟(如内存访问延迟),通过切换不同的 Warps 来保持执行单元的高利用率。
调度器的吞吐执行能力
- “32 threads/clk”,每个时钟周期,Warp Scheduler 最多可以发射一个 Warp(即 32 个线程)去执行。
- SM 有 4 个 warp scheduler,理论上可以每个时钟周期调度 4 个 warp(128 个线程)
- 这代表的是 执行能力的上限,而不是它能同时“管理”的 Warp 数量。
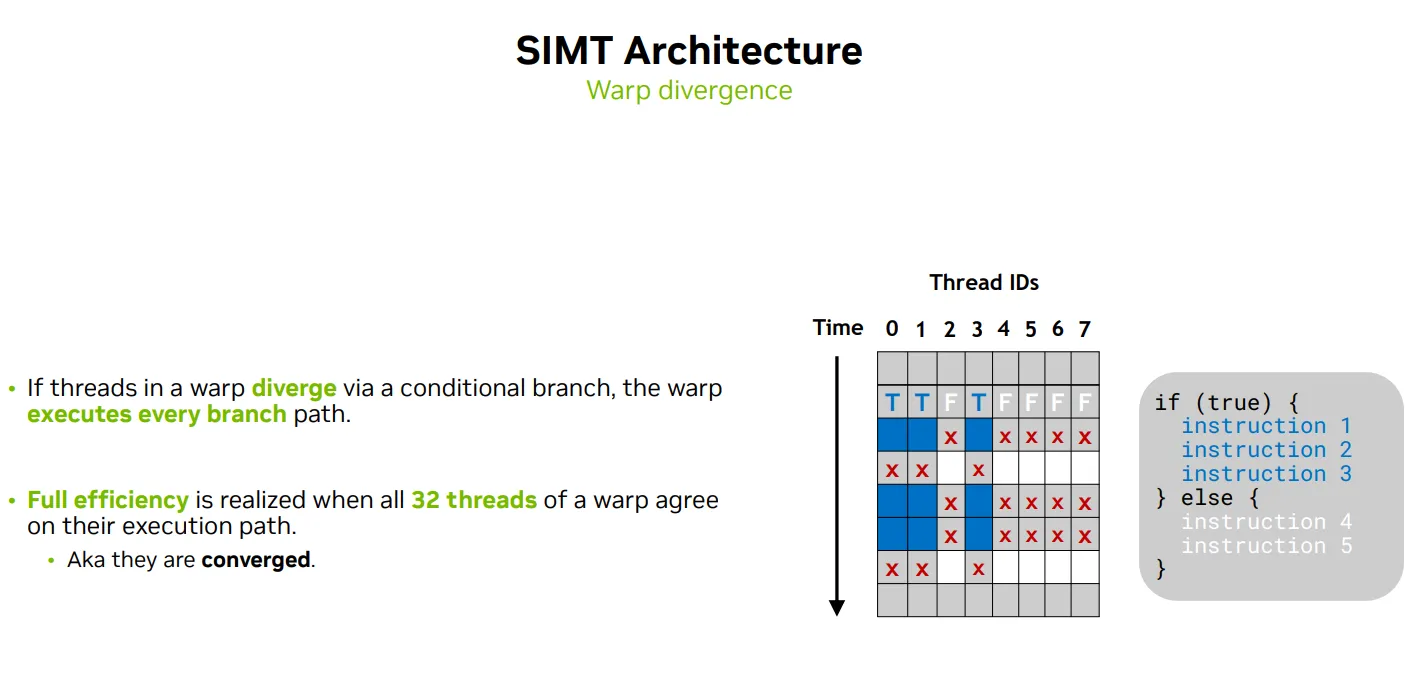
SIMT下WARP的问题
-
Single instruction, 一个warp里的线程通常执行相同的指令
-
Warp是基本调度单位, Threads in a warp may diverge
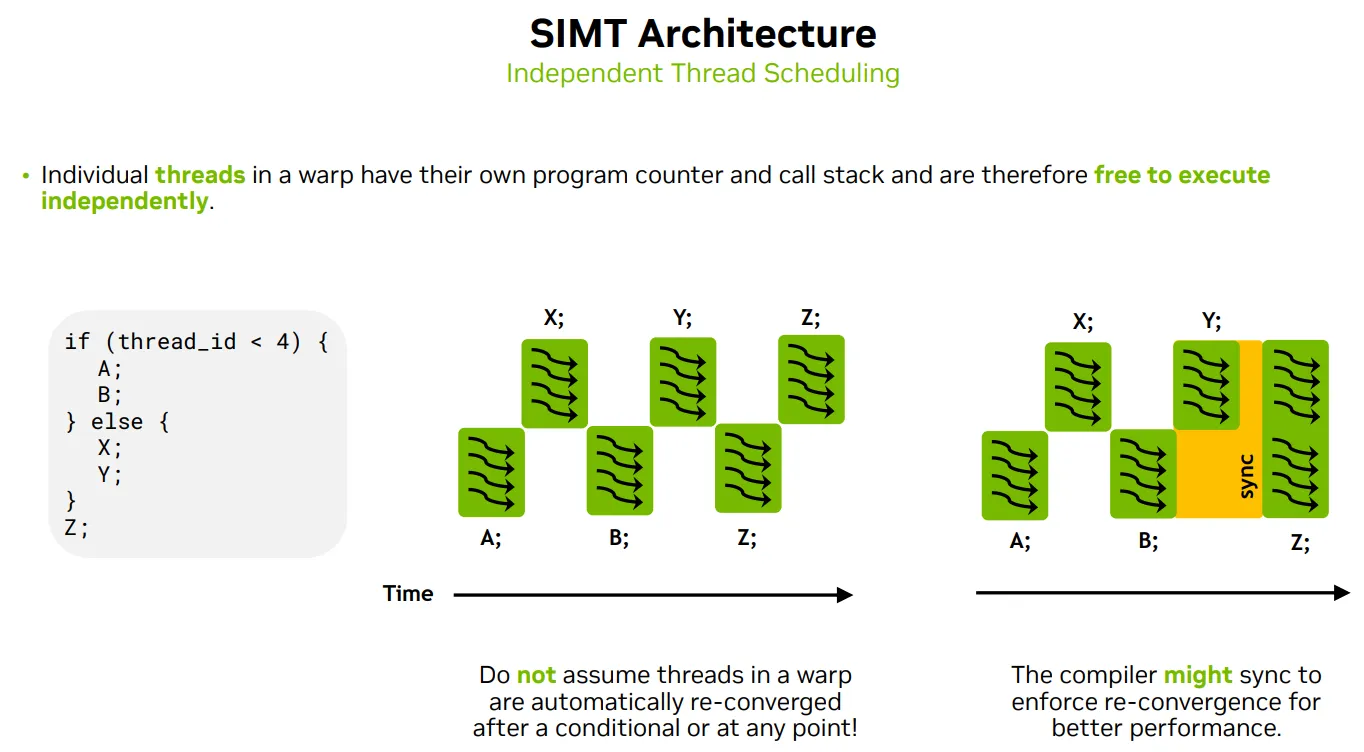
-
Multiple threads, 一个warp里的线程通常处理不同的数据
-
Warp是基本调度单位, Threads in a warp execute independently asyncly
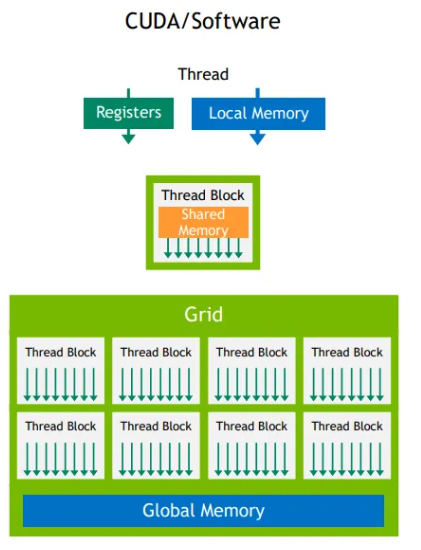
Programming POV(线程的逻辑结构Thread Hierachy): focus SPMD than CUDA Programming Model
Kernel
Threads use their unique thread index to work on disjoint data
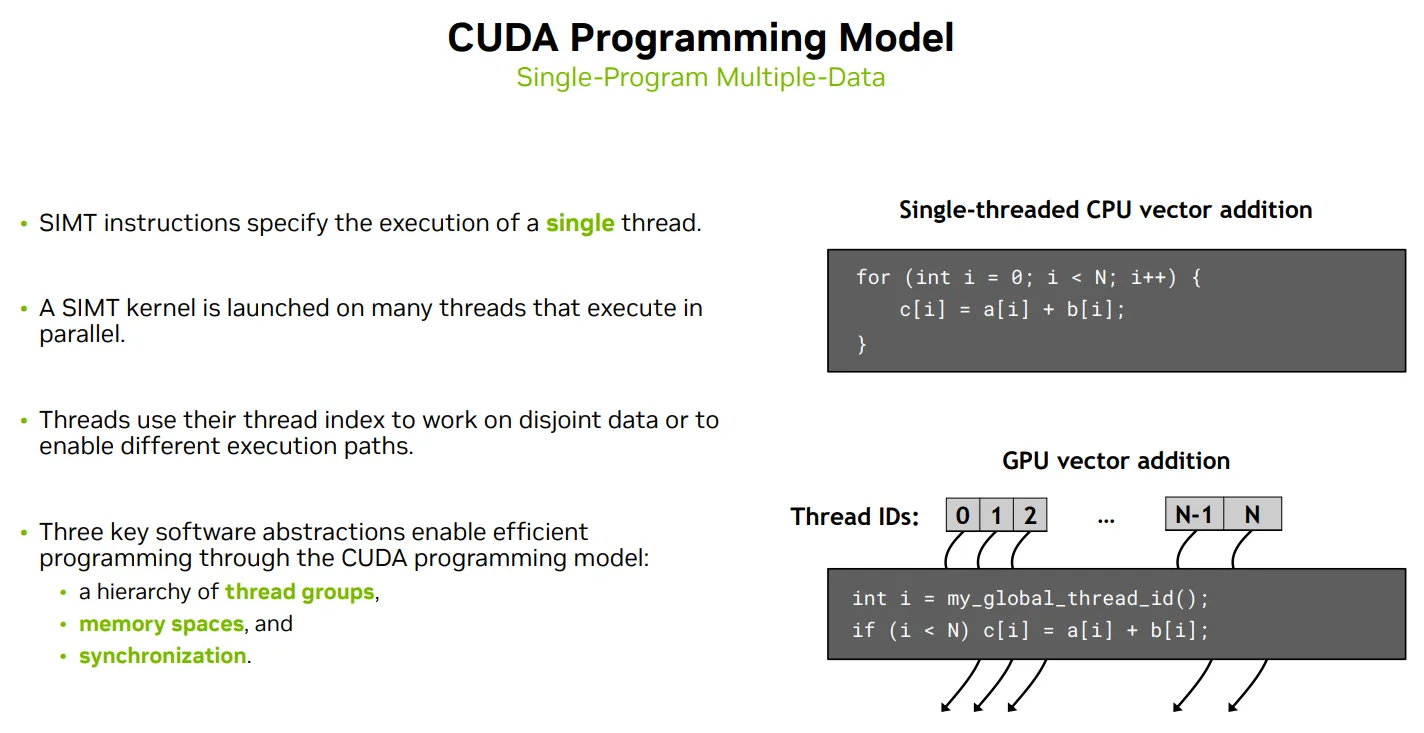
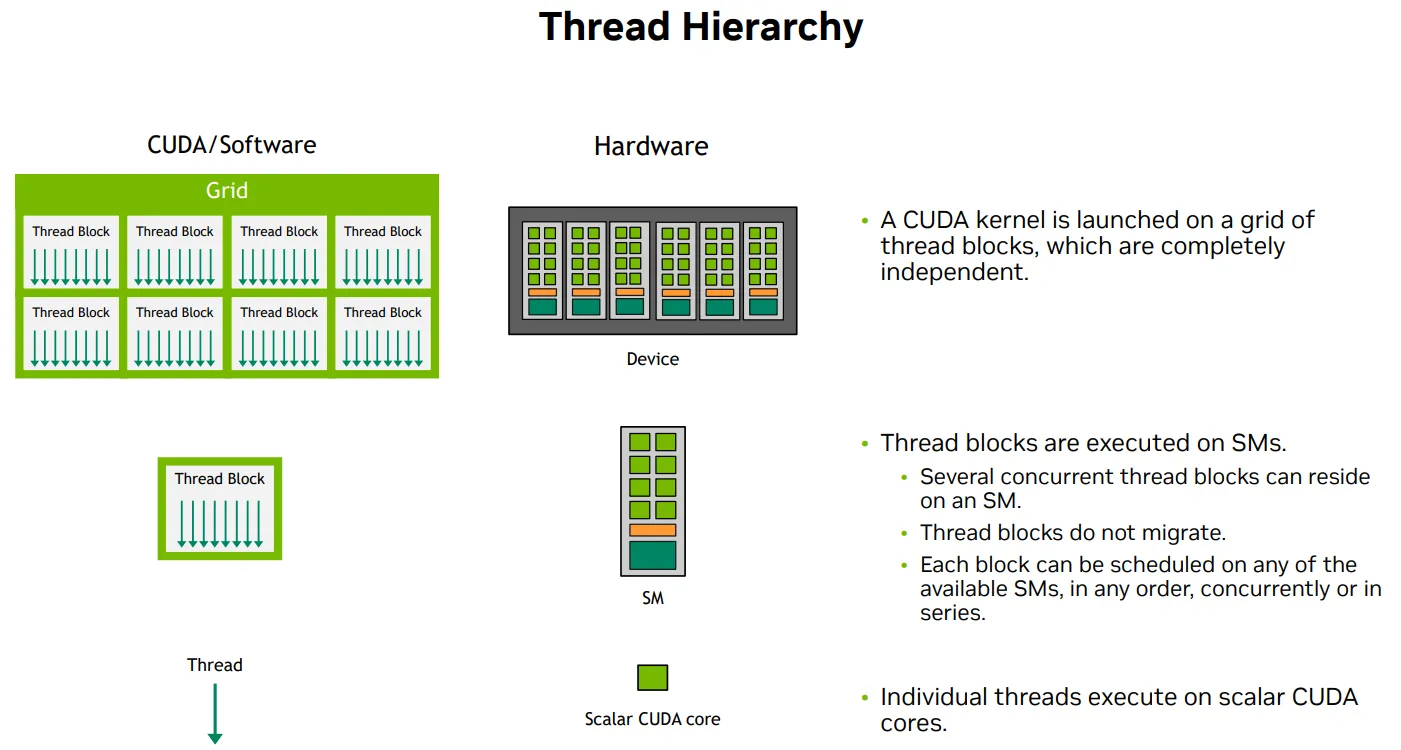
Thread Hierachy to orchestration to HW
- Kernel is launched on a grid of thread blocks, which are completely independent, on GPU
- Optional level of Thread block clusters 跨 Thread Block 的共享内存访问,跨 SM 的线程块协作
- Several thread blocks are executed concurently on one SM
- At runtime, thread block is divided into warps for SIMT execution
- The way of partition is always the same: each warp conatins threads of consective, increasing thread IDs with the first wap containing thread 0.
- Thread executes on core
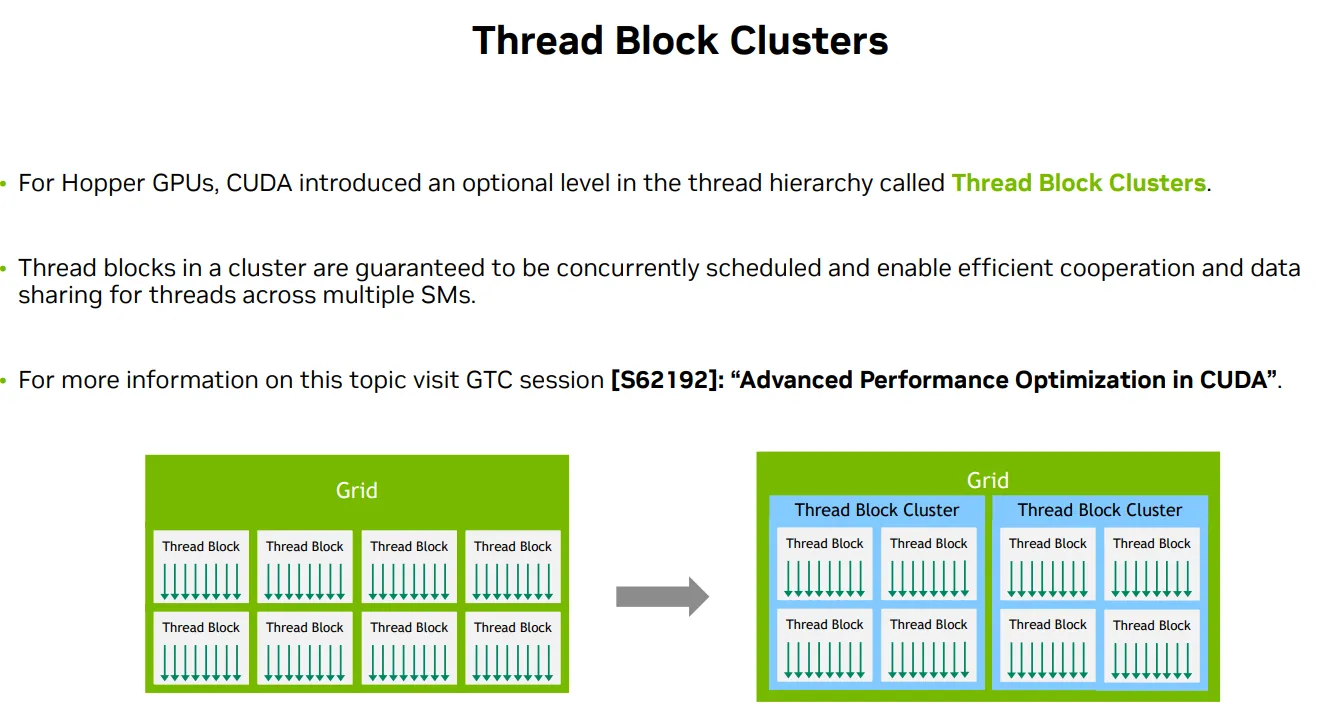
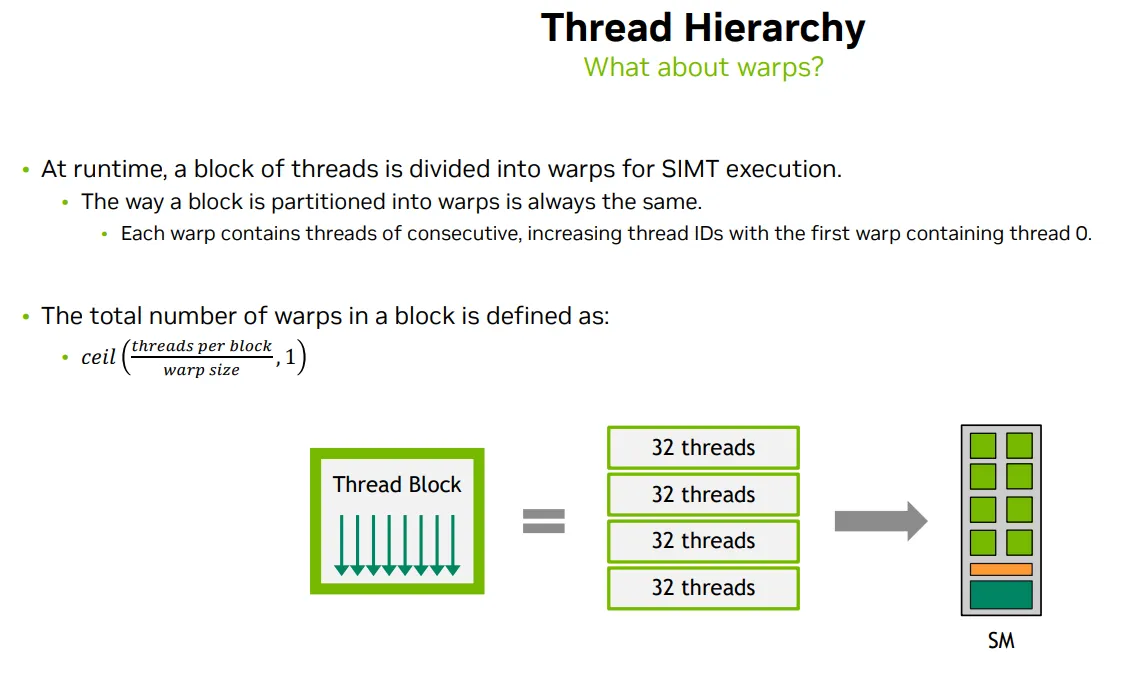
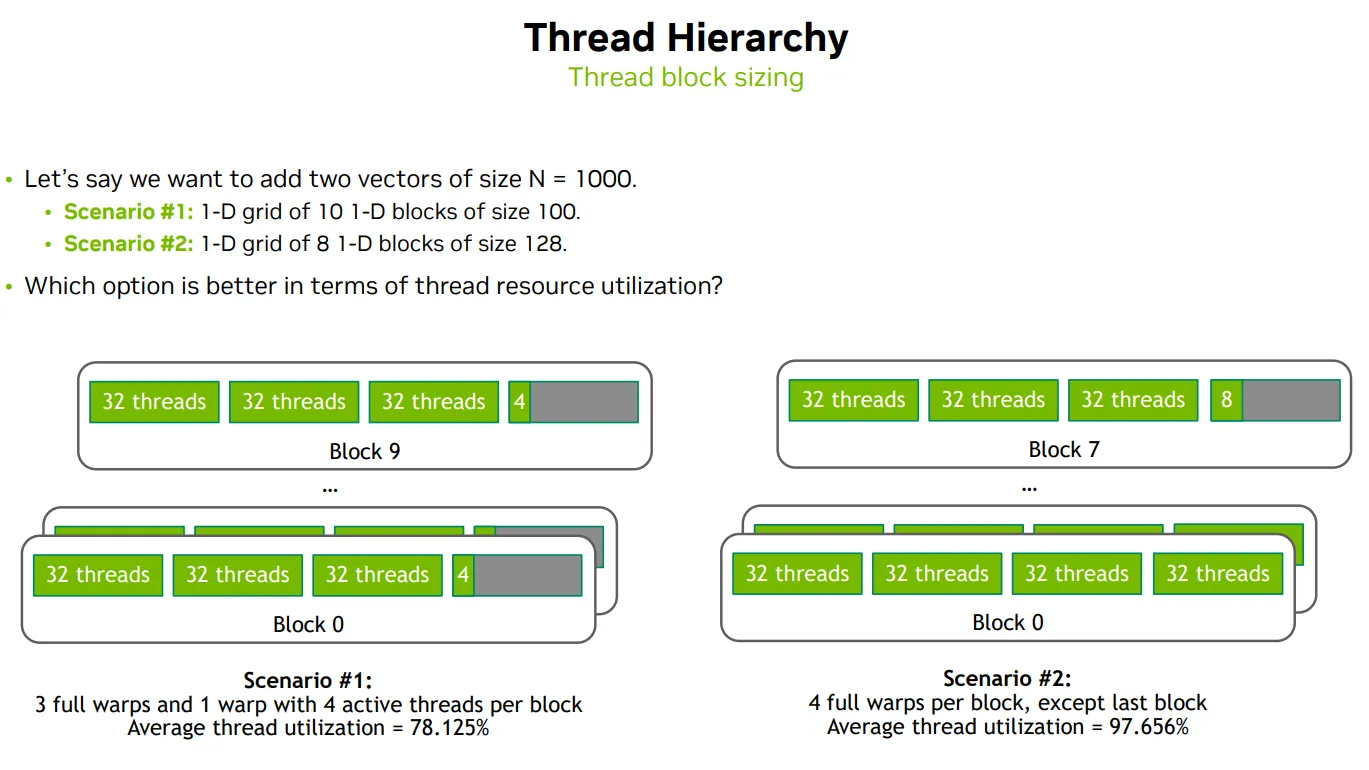
Thread block sizing
| 变量 | 含义 | 值 |
|---|---|---|
| gridDim.x | 网格在 x 方向上的 block 数量 | 10 |
| blockDim.x | 每个 block 中的线程数 | 100 |
Memory Hierachy
Logical thread corresponding Memory hierarchy
| Logical thread | Mem | HW |
|---|---|---|
| Per-thread | 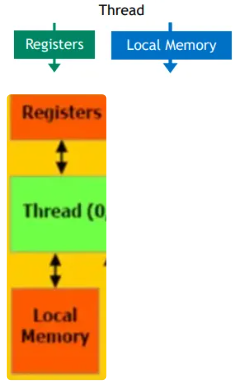 |
 |
| Per-block | 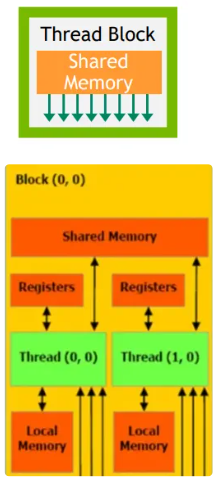 |
 |
| Per-grid | 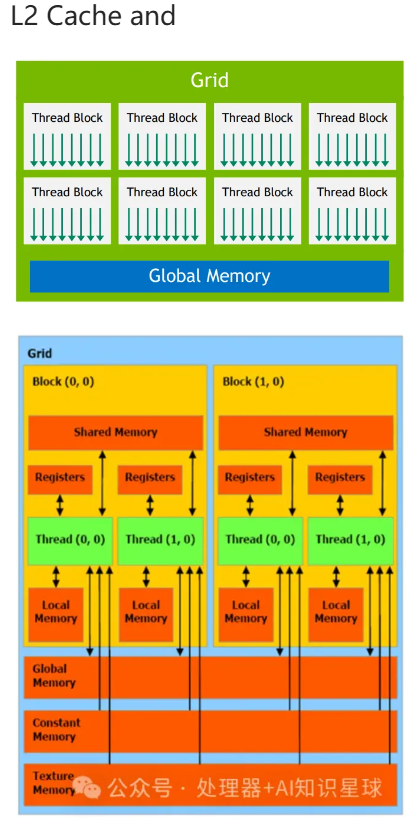 |
 |
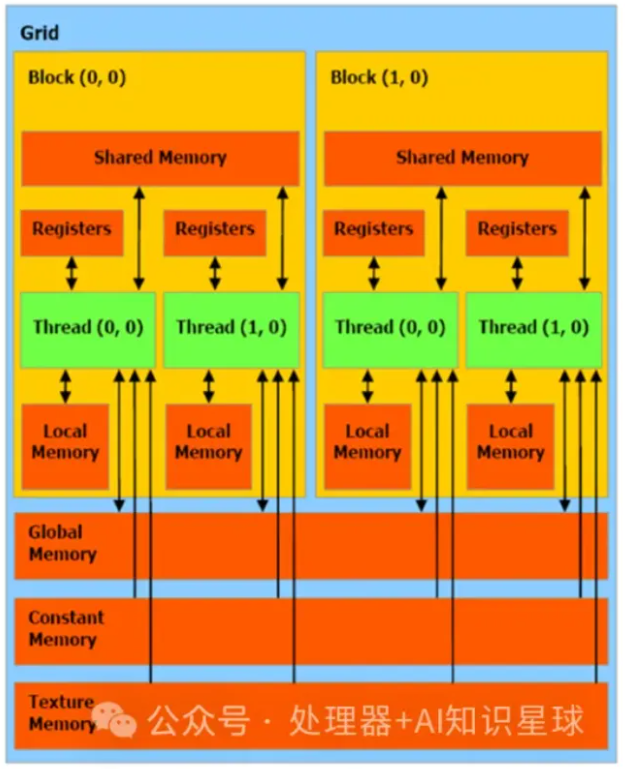
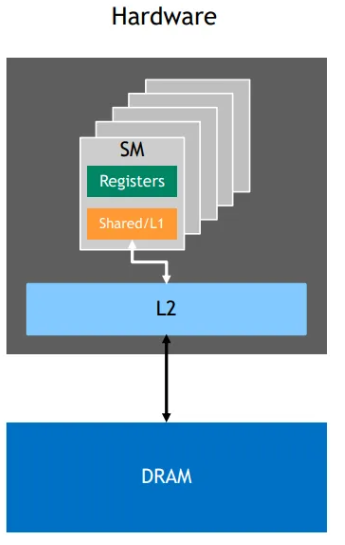
Shared mem
// 共享内存,仅限 Block 内访问
__shared__ float sharedData[BLOCK_SIZE];
sharedData[i];
Global mem
// 在设备上分配内存
cudaMalloc(void** devPtr, size_t size);
// 释放设备内存
cudaFree(void* devPtr);
float *d_input;
cudaMalloc((void**)&d_input, 256 * sizeof(float));
d_input[i];
cudaFree(d_input);
CPU-GPU Unified Memory
| CPU-GPU Unified Memory(统一内存 | Non-Unified Memory非统一内存 | |
|---|---|---|
| 地址空间 | 单一地址空间:CPU 和 GPU 共享 同一个虚拟地址空间 | 独立地址空间 |
| 数据迁移 | 自动数据迁移:当 GPU 访问 CPU 端的数据时,CUDA 会自动将数据迁移到 GPU 端,反之亦然。 | 手动数据迁移 cudaMemcpy |
// 分配托管内存
cudaMallocManaged(void** devPtr, size_t size);
//提前预取数据
cudaMemPrefetchAsync(void* devPtr, size_t size, int device, cudaStream_t stream);
// 从主机复制到设备
cudaMemcpy(void* dst, const void* src, size_t size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
// 从设备复制到主机
cudaMemcpy(void* dst, const void* src, size_t size, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
// 设备内存之间复制
cudaMemcpy(void* dst, const void* src, size_t size, cudaMemcpyDeviceToDevice);
// 没有提前预取
// 异步内存复制
cudaMemcpyAsync(void* dst, const void* src, size_t size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, cudaStream_t stream);